
What Is Network Segmentation, and Why Does It Matter?
Network segmentation (also called network partitioning or isolation) is the practice of dividing a network into smaller, controlled segments to enhance security, optimize performance, and improve regulatory compliance. Instead of allowing free movement across an entire network, segmentation creates barriers that restrict access based on predefined rules, significantly reducing the risk of cyberattacks and data breaches.
For businesses, this means greater control over sensitive data, improved threat detection, and reduced attack surfaces. Without segmentation, a flat network—where all systems and users are interconnected—creates an environment where attackers can move laterally with ease. A single compromised endpoint can quickly lead to full network infiltration, putting customer data, proprietary information, and critical business operations at risk.
With proper segmentation, businesses can:
Limit the impact of cyberattacks by confining breaches to isolated network sections.
Enhance compliance with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS by restricting access to sensitive data.
Improve network performance by reducing congestion and ensuring mission-critical applications get priority bandwidth.
Streamline security management by enabling targeted monitoring, detection, and response to threats.
What Is an Example of a Network Segment?There are several ways to implement network segmentation, each with its own advantages and use cases. Typically, organizations achieve segmentation through methods such as firewalls, Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs), Software Defined Networking (SDN), and role-based segmentation.Role-Based Segmentation: One common approach is segmenting a network based on user roles and access requirements. For example, in a corporate environment, the network can be divided into separate segments for different departments. The finance team’s segment is restricted to accounting software and payroll systems, while the marketing team has access to campaign tools and creative assets. This minimizes the risk of data leaks and insider threats by ensuring that employees can only access the resources necessary for their work.VLAN Segmentation: VLANs or subnets are widely used to divide a network into smaller segments. VLANs create logical groups of devices that communicate as if they were on the same physical network, while subnets use IP addressing to organize and separate traffic. While effective, this type of segmentation often requires substantial reconfiguration and ongoing maintenance.Firewall Segmentation: Firewalls can be deployed within a network to establish internal security zones. For instance, a data center may use firewalls to isolate sensitive customer databases from public-facing web servers, ensuring that external threats cannot easily reach critical systems.SDN Segmentation: A more modern approach involves leveraging Software Defined Networking (SDN) to create dynamic network overlays. SDN automates segmentation and enhances micro-segmentation, though it can introduce additional complexity in deployment and management.Each segmentation method offers unique security and operational benefits, making it essential for businesses to choose an approach that aligns with their infrastructure and security requirements.The Key Benefits of Network SegmentationNetwork segmentation is not just about security—it is about efficiency, control, and resilience. It allows businesses to operate with confidence, knowing that critical systems are protected, performance is optimized, and compliance requirements are met. As cyber threats evolve, segmentation remains one of the smartest investments a company can make to secure its digital environment. But the benefits go far beyond just security—network segmentation also enhances visibility, simplifies compliance, and optimizes resource allocation. Here is how:1. Stronger Security with Built-in ContainmentA segmented network prevents attackers from moving freely if they breach a system. Instead of having access to everything, they are trapped within a confined area, reducing the risk of a full-scale attack. This approach is especially effective against ransomware, which relies on lateral movement to encrypt entire networks.2. Faster Threat Detection and ResponseSecurity teams can isolate and analyze suspicious activity more easily when a network is segmented. If a breach occurs, IT teams can quickly pinpoint which segment is affected, contain the issue, and prevent it from spreading. This reduces downtime, minimizes damage, and speeds up recovery.3. Less Congestion, Better PerformanceA network that routes all traffic through the same channels gets bogged down quickly. Segmentation directs data only where it is needed, reducing unnecessary load and keeping critical applications running smoothly. For businesses that rely on real-time data processing—like financial services or healthcare—this can mean the difference between seamless operations and frustrating slowdowns.4. Easier Compliance with Industry RegulationsRegulatory frameworks like HIPAA, PCI-DSS, and GDPR require strict control over sensitive data. Segmentation makes compliance easier by keeping regulated information separate from general network traffic. This not only simplifies audits but also lowers the risk of costly violations and data breaches.5. Limited Impact of CyberattacksAn unsegmented network is like a house with no doors—once an attacker gets in, they have free reign. Network segmentation creates controlled barriers, ensuring that even if one part of the system is compromised, the rest remains protected. This significantly reduces downtime and financial losses in the event of an attack.6. More Control Over Who Can Access WhatNot every employee, vendor, or device needs access to all parts of a network. Segmentation allows businesses to create access rules based on job roles, departments, or security levels. This prevents unauthorized access and protects sensitive areas from both external hackers and insider threats.7. Scales with Your Business Without Added ComplexityAs a company grows, its network infrastructure must scale with it. Without segmentation, expanding IT systems becomes chaotic. Segmented networks make it easier to add new devices, locations, or cloud services without overloading existing resources or creating new security gaps.7 Best Practices for Effective Network SegmentationA well-planned network segmentation strategy enhances security, optimizes performance, and simplifies compliance. However, improper implementation can lead to unnecessary complexity, weak points, or inefficient workflows. To get the most out of network segmentation, follow these best practices:1. Enforce the Principle of Least PrivilegeEvery user and system should have only the access they need—nothing more. Applying role-based access control (RBAC) and least privilege principles reduces the risk of unauthorized access and minimizes exposure to potential threats. This approach ensures that even if an account is compromised, an attacker’s reach is limited. Regularly review access permissions to prevent privilege creep.2. Limit Third-Party AccessThird-party vendors, contractors, and external partners are often targeted by attackers looking for weak links. Instead of granting broad access, isolate their permissions to specific network segments. Use zero-trust principles, enforce multi-factor authentication (MFA), and require vendors to connect through secure portals with restricted privileges. This prevents third parties from becoming a gateway to critical systems.3. Continuously Audit and Monitor Network SegmentsWithout ongoing monitoring, security gaps can go unnoticed until a breach occurs. Use real-time network monitoring tools to track traffic patterns and detect anomalies. Regular security audits and compliance checks ensure that segmentation policies remain effective. If unauthorized activity is detected, rapid containment measures should be in place to isolate the affected segment.4. Design Secure and Intuitive Access PathsA well-segmented network does not only block threats—it also ensures smooth and secure access for authorized users. Avoid overly complex routing that forces employees to use workarounds, as this can create unintended vulnerabilities. Map out logical access paths, restrict lateral movement between segments, and implement firewalls and micro-segmentation policies to control traffic flow efficiently.5. Group Similar Network Resources TogetherSegmentation should be based on data sensitivity, function, and risk level. For example, keep internal databases separate from public-facing applications, and segment IoT devices away from core systems. By grouping similar resources together, businesses can reduce security overhead, streamline policy enforcement, and simplify incident response.6. Avoid Over-SegmentationWhile segmentation improves security, too many micro-segments can backfire by making the network harder to manage, increasing latency, and complicating IT operations. Strike a balance between security and usability by grouping resources logically. When defining segments, ask:Does this segmentation add real security value?Will it slow down workflows or increase operational complexity?Can automation help manage policy enforcement?7. Visualize Your Network ArchitectureWithout clear visibility, managing network segmentation becomes a guessing game. Use network mapping tools to create an accurate, real-time overview of all segments, traffic flows, and access points. Automated visualization tools help security teams detect misconfigurations, optimize policies, and quickly identify vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.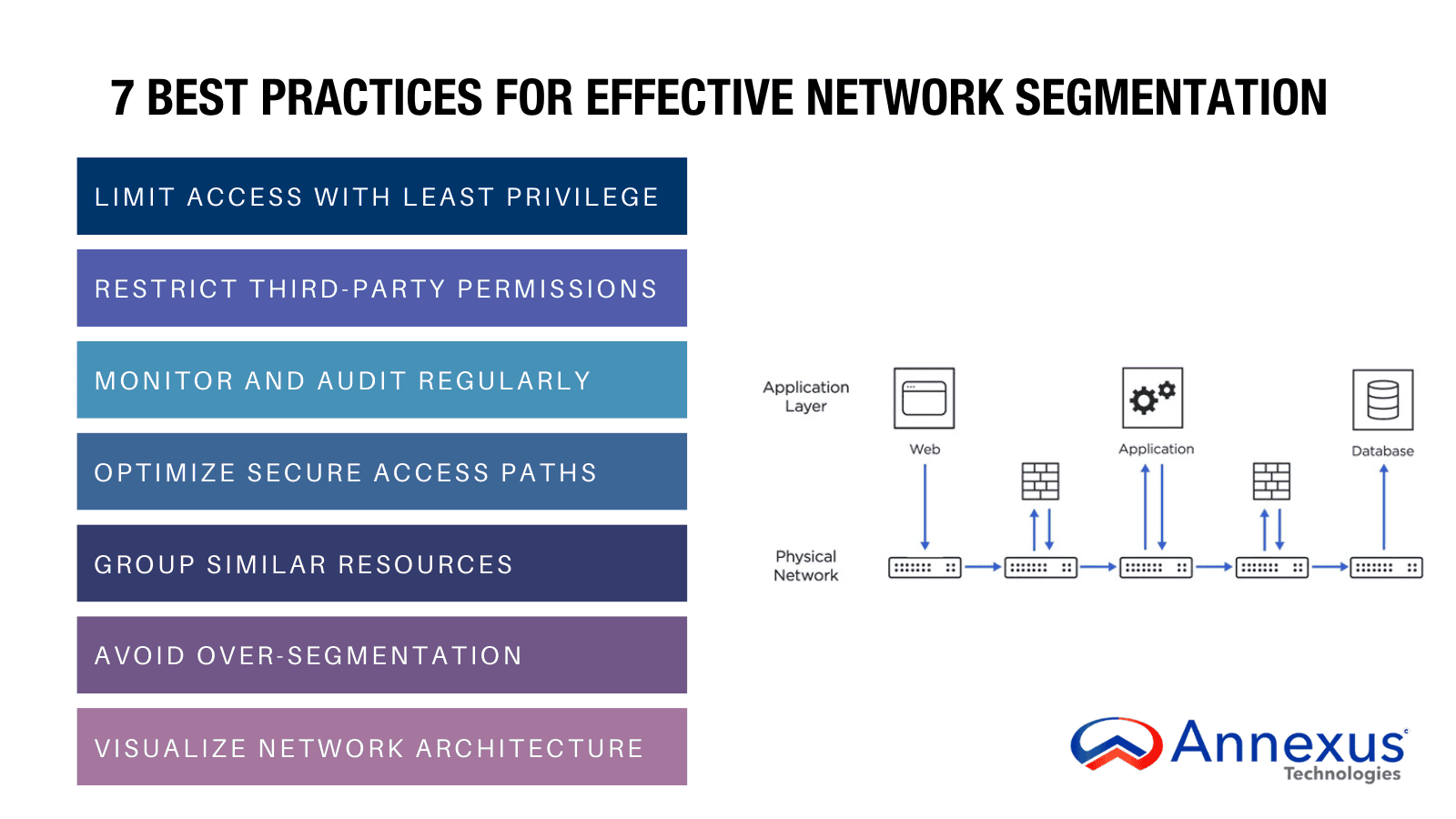 The Future of Network SegmentationTraditional segmentation methods, like VPNs, struggle to keep up with the demands of modern networks. As businesses grow and cyber threats evolve, Software-Defined Networking (SDN) is emerging as a more scalable and secure alternative. SDN enables:Granular Access Control – Enforces least privilege policies across all systems.Reduced Attack Surface – Restricts unauthorized access while maintaining efficiency.Advanced Audit Trails – Provides detailed logs for forensic analysis and compliance.A well-segmented network is key to protecting your business from cyber threats while ensuring seamless operations. Annexus Technologies specializes in designing tailored, high-performance network security solutions that safeguard critical assets and enhance compliance. Contact us today to explore how our expertise can help you build a more secure and resilient network.
The Future of Network SegmentationTraditional segmentation methods, like VPNs, struggle to keep up with the demands of modern networks. As businesses grow and cyber threats evolve, Software-Defined Networking (SDN) is emerging as a more scalable and secure alternative. SDN enables:Granular Access Control – Enforces least privilege policies across all systems.Reduced Attack Surface – Restricts unauthorized access while maintaining efficiency.Advanced Audit Trails – Provides detailed logs for forensic analysis and compliance.A well-segmented network is key to protecting your business from cyber threats while ensuring seamless operations. Annexus Technologies specializes in designing tailored, high-performance network security solutions that safeguard critical assets and enhance compliance. Contact us today to explore how our expertise can help you build a more secure and resilient network.

